Introduction
Overview of central HVAC systems and their importance
Central HVAC systems are the most common type of heating and cooling systems used in residential and commercial buildings. They are designed to provide controlled heating, cooling, and ventilation throughout the entire building. The importance of a central HVAC system lies in its ability to maintain a comfortable indoor environment regardless of the weather conditions outside.
Basic components of central HVAC systems
A central HVAC system consists of several key components:
- Thermostat: This is the control panel where you can set the desired temperature.
- Heating unit: In cooler months, the heating unit, which can be a furnace or a heat pump, generates heat to warm the air.
- Cooling unit: During warmer months, the cooling unit, typically an air conditioner, cools the air by removing heat and humidity.
- Ductwork: Ducts are used to distribute the heated or cooled air throughout the building.
- Air filters: These filters help clean the air by trapping dust, allergens, and other particles.
How central HVAC systems regulate temperature and air quality
Central HVAC systems regulate temperature and air quality through a process called air exchange. Here’s how it works:
- The thermostat detects the current temperature and compares it to the desired temperature set by the user.
- If the current temperature is lower than the desired temperature, the heating unit is activated. It warms the air, which is then distributed through the ductwork to each room.
- Conversely, if the current temperature is higher than the desired temperature, the cooling unit is activated. It cools the air and removes excess humidity before distributing it through the ductwork.
- The air filters help remove dust, allergens, and other particles from the air, improving indoor air quality.
Central HVAC systems operate on a cycle, constantly monitoring and adjusting the temperature to maintain a comfortable indoor environment. Modern central HVAC systems may also have additional features such as zoning, which allows for customized temperature control in different areas of the building.
Understanding how central HVAC systems work can help you make informed decisions when it comes to maintenance, repairs, or upgrades. Regular maintenance, including changing air filters and scheduling professional inspections, is essential to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
Cooling Process
Understanding how central HVAC systems cool the air
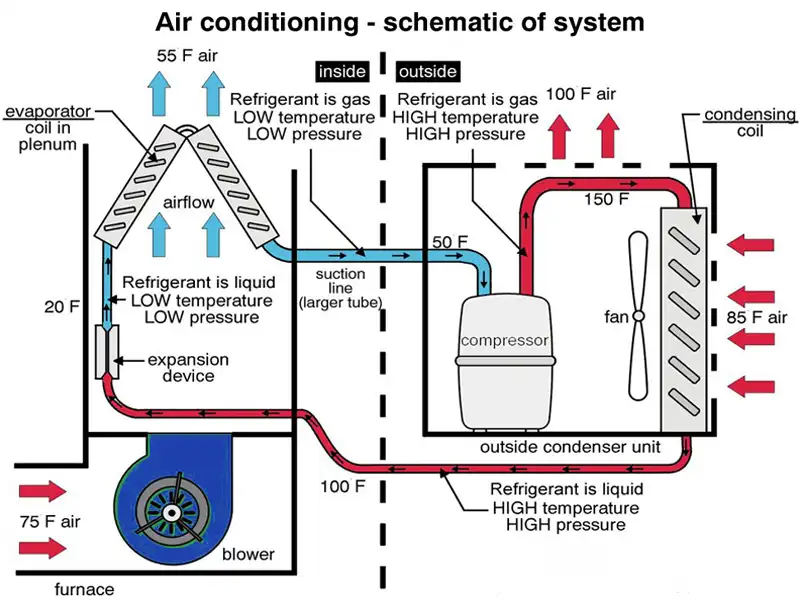
Central HVAC systems are designed to efficiently cool the air in a building, whether it’s a home, office, or commercial space. The cooling process begins with the air handler unit, which contains a blower fan and evaporator coil. The blower fan draws warm air from the building into the HVAC system, and the evaporator coil cools the air down by removing heat from it. This cooled air is then distributed back into the building through air ducts and vents.
Condenser coils and refrigerant in central HVAC systems
In the cooling process, condenser coils play a crucial role. These coils are located in the outdoor unit of the HVAC system and are responsible for releasing heat from the refrigerant. Refrigerant is a special chemical that flows through the HVAC system, absorbing and releasing heat to cool the air. As the warm air from the building flows over the evaporator coil, the refrigerant inside the coil absorbs the heat from the air, cooling it down. The refrigerant then moves to the condenser coils, where it releases the heat it absorbed to the outside air.
Role of the compressor in the cooling process
The compressor is another essential component of central HVAC systems. Its function is to increase the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant, which allows it to absorb more heat from the air. The compressor takes low-pressure, cool refrigerant from the evaporator coil and compresses it into high-pressure, hot refrigerant gas. This gas then flows into the condenser coils, where it releases the heat and becomes a high-pressure liquid. The liquid refrigerant then moves back into the evaporator coil to repeat the cooling process.
By understanding how central HVAC systems cool the air, you can better appreciate the engineering and technology behind these systems. It’s important to keep your HVAC system properly maintained to ensure that it continues to effectively cool the air in your building. Regular inspections, filter changes, and professional maintenance can help keep your central HVAC system running smoothly and efficiently.
Heating Process
Explanation of how central HVAC systems provide heat
Central HVAC systems are designed to provide effective heating solutions for homes and commercial buildings. The process starts with a heating source, which is usually a furnace or a heat pump. These heating sources generate heat by burning fuel or using electricity, respectively. The heat produced is then distributed throughout the building using a system of ductwork and vents. The central HVAC system also includes a thermostat that allows users to control the temperature and ensure optimal comfort.
Furnace and heat exchanger in central HVAC systems
In central HVAC systems that use a furnace, the combustion process takes place inside the furnace. This process involves burning fuel, such as natural gas, oil, or propane, to produce heat. The heat exchanger in the furnace transfers the heat from the combustion process to the air that circulates throughout the building. The heated air is then distributed through the ductwork and vents to provide warmth in different areas.
For central HVAC systems that use a heat pump, the heating process is a bit different. Instead of burning fuel, a heat pump extracts heat from the outside air or the ground. The heat is then transferred to the refrigerant inside the heat pump, which is then compressed to increase its temperature. The heated refrigerant is then used to warm the air that is circulated inside the building.
Thermostat control for heating in central HVAC systems
The thermostat plays a crucial role in controlling the heating process in central HVAC systems. It allows users to set the desired temperature and enables the system to maintain that temperature by turning the heating source on or off when needed. Modern thermostats offer advanced features such as programmable schedules, which allow for energy-saving settings by adjusting the temperature based on occupancy patterns. Some thermostats can also be controlled remotely through smartphones or other devices, providing convenience and flexibility.
In conclusion, central HVAC systems provide heating by utilizing a heating source, such as a furnace or a heat pump, to generate heat. The heat is then distributed throughout the building using ductwork and vents. A thermostat allows users to control the temperature and ensures comfort and energy efficiency. Understanding how central HVAC systems work can help users make informed decisions about their heating needs and maximize the performance of their HVAC systems.
Ventilation and Air Circulation
Importance of ventilation in central HVAC systems
In any central HVAC system, ventilation plays a critical role in maintaining indoor air quality and creating a comfortable space. Without proper ventilation, the air can become stale and filled with pollutants, leading to various health issues. Ventilation brings in fresh outdoor air and removes indoor pollutants, ensuring a healthy and safe environment for occupants.
Air ducts and registers in central HVAC systems
A central HVAC system uses a network of air ducts and registers to distribute conditioned air throughout the building. These ducts act as pathways, carrying the heated or cooled air from the HVAC unit to different rooms. Registers, typically located on walls or ceilings, provide an outlet for the conditioned air to enter the room. By strategically placing the registers, the airflow can be directed and adjusted for optimal comfort.
How central HVAC systems circulate and filter air
Central HVAC systems circulate air by pulling in air from the return ducts, passing it through the HVAC unit for conditioning, and then releasing it back into the space through the supply ducts. As the air flows through the HVAC unit, it goes through a filtration system that removes dust, allergens, and other particles. This filtration process helps improve indoor air quality by reducing airborne contaminants and potential health hazards.
With advancements in technology, many central HVAC systems now incorporate high-efficiency filters that can capture even smaller particles. This is especially beneficial for individuals with allergies or respiratory issues, as it helps reduce their exposure to airborne irritants.
By understanding how central HVAC systems work, you can better appreciate the importance of proper ventilation and air circulation in maintaining a comfortable and healthy indoor environment. Regular maintenance, including air duct cleaning, replacing filters, is essential to ensure the efficiency and effectiveness of the system.
Energy Efficiency and Control
Efficiency ratings for central HVAC systems
Central HVAC systems play a crucial role in maintaining a comfortable indoor environment all year round. However, not all systems are created equal when it comes to energy efficiency. Understanding efficiency ratings can help you make an informed decision when choosing a central HVAC system for your home or business.
Efficiency ratings are measured by two important metrics: SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) and AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency). SEER measures the cooling efficiency of an air conditioner or heat pump, while AFUE measures the heating efficiency of a furnace or boiler.
The higher the SEER or AFUE rating, the more energy-efficient the system is. Investing in a system with higher efficiency ratings can lead to significant energy savings and lower utility bills in the long run.
Smart thermostats and energy-saving features
In addition to choosing an energy-efficient central HVAC system, the use of smart thermostats and energy-saving features can further enhance control and efficiency.
Smart thermostats allow users to program and control their HVAC system remotely through a smartphone or other smart devices. These devices offer features like scheduling, which allows you to set specific temperature settings at different times of the day, optimizing energy usage. Some smart thermostats even analyze your usage patterns and make automatic adjustments to maximize energy efficiency.
Energy-saving features, such as zoning and variable-speed technology, also contribute to energy efficiency. Zoning allows you to divide your home or business into different areas or zones, each with its own temperature controls. This way, you can avoid heating or cooling unoccupied rooms, saving energy. Variable-speed technology adjusts the system’s output based on the actual needs, reducing energy waste and maintaining optimal comfort.
Importance of regular maintenance for optimal performance
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring that your central HVAC system operates at its peak performance and energy efficiency. It includes tasks like ductwork cleaning, replacing air filters, checking refrigerant levels, inspecting electrical connections, and lubricating moving parts.
By maintaining your system regularly, you can prevent breakdowns, extend its lifespan, and optimize energy efficiency. Additionally, regular maintenance improves indoor air quality by ensuring proper airflow and reducing the accumulation of dust and allergens.
Investing in an energy-efficient central HVAC system and utilizing smart thermostats and energy-saving features can significantly improve control and reduce energy consumption. However, regular maintenance is the key to keeping your system running smoothly and efficiently for years to come.
Advantages of central HVAC systems
Central HVAC systems offer several advantages over other heating and cooling options:
- Consistent temperature control: Central HVAC systems provide even heating and cooling throughout the building, ensuring a comfortable environment in every room.
- Energy efficiency: These systems are designed to be highly efficient, which can lead to cost savings on utility bills.
- Improved indoor air quality: Central HVAC systems often include filters that remove dust, allergens, and other pollutants from the air, resulting in cleaner and healthier indoor air.
Factors to consider when choosing a central HVAC system
When selecting a central HVAC system for your home or business, it’s important to consider the following factors:
- Size: The system should be appropriately sized for your building to ensure efficient operation and optimal comfort.
- Energy efficiency: Look for systems with high SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings to maximize energy savings.
- Maintenance requirements: Consider the maintenance needs of the system and choose one that is easy to service and maintain.
In conclusion, central HVAC systems provide consistent and efficient heating, ventilation, and air conditioning throughout a building. They offer advantages such as temperature control, energy efficiency, and improved indoor air quality. When choosing a system, consider factors such as size, energy efficiency, and maintenance requirements to ensure optimal performance and comfort.